Support and resources
We are delighted to share a suite of resources which have been developed to support the MCAS community.
Our aim is to provide comprehensive support and valuable information to help individuals navigate and manage their condition effectively. You will find self-management resources, information about symptoms and triggers, wellbeing resources and specific resources for supporting children in schools and secondary schools, and reasonable adjustments in the workplace.
We continue to develop resources which we hope will support the MCAS community in even more effective ways, so please keep an eye on our resources page for updates. Your feedback is invaluable to us, and we encourage you to share your suggestions of resources you feel would be beneficial.

MCAS Brochure
Our MCAS medical brochure has been developed in collaboration with medical specialists in mast cell disorders.
It includes the latest published consensus findings for diagnosing MCAS, alongside patient case examples and information on medical management.
You may find this a useful tool in introducing colleagues to MCAS.
Download the brochure in colour here.
Download the brochure in black & white here.

Biomarker tests for MCAS
In 2021, Dr Bethan Myers presented her research on biomarker tests for MCAS at the British Society for Haematology meeting.
The main aims of this study were to assess urinary PG levels and NMH levels across the MCDs and compare results of urinary PGs & NMH across all the MCDs. A secondary aim was to assess the importance of keeping the samples chilled throughout collection and transit.
The results demonstrate that all mast cell disorders (except CM) have similarities in having higher levels of one or more prostaglandins known to be produced by mast cells.
Download a copy of her poster here.
You can watch a video presentation of her research here.
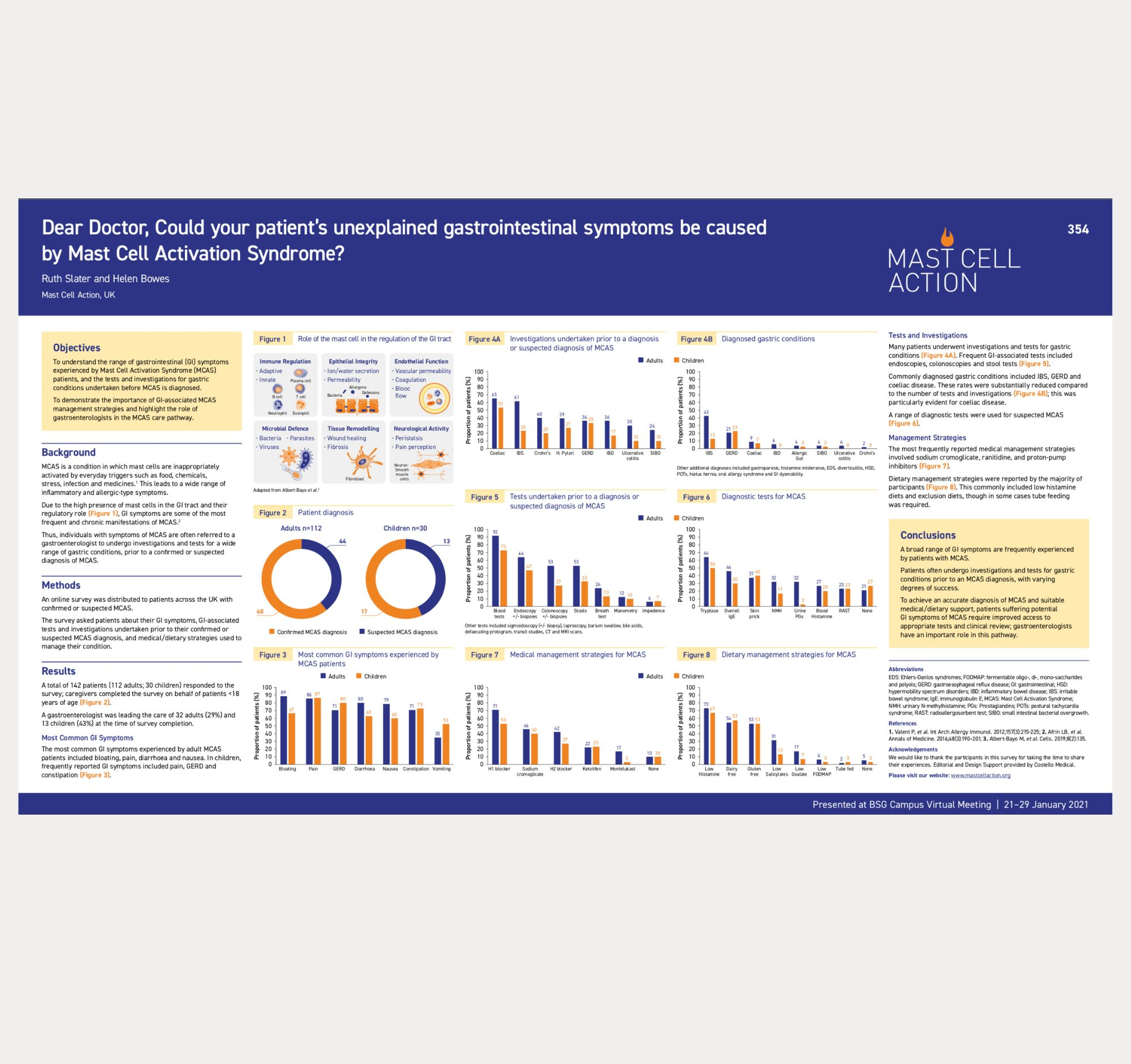
Gastrointestinal symptoms and MCAS poster
Our latest research into both adult and paediatric experiences of MCAS and gastrointestinal symptoms was recently presented at the British Society of Gastroenterology 2021.
Our research concluded that a broad range of gastrointestinal symptoms are frequently experienced with MCAS. Patients often undergo investigations and tests for gastric conditions prior to an MCAS diagnosis, with varying degrees of success.
To achieve an accurate diagnosis of MCAS, patients require improved access to appropriate tests and clinical review.
You can download a copy of the poster here, or listen to a presentation of the poster here.

Ehlers Danlos Syndromes Toolkit
The Royal College of GPs has developed an Ehlers Danlos Syndromes (EDS) Toolkit that has a section on MCAS under Emerging Major Associations.
The Toolkit has been created for primary healthcare professionals, patients and carers.
This toolkit can be used to assist in the delivery of safe and effective care to patients.
You can access the toolkit here.
Resources for medical professionals
We believe these resources will be helpful in understanding MCAS and providing practical advice for diagnosis and treatment of mast cell activation syndrome.
MCAS presentations
The following listed presentations are available to watch online and have been given by doctors and researchers across multiple disciplines who have specialised in MCAS.
- 'Mast cell activation' presented by Dr. Anne Maitland from the ICAHN school of medicine at Mount Sinai
- Treatment of Allergy and Immunology Issues by Dr. Anne Maitland presented at the EDS virtual Summer conference 2020
- Dr Alex Croom presents on MCAS at the POTs Masterclass 2019
- Dr Bethan Myers presents on MCAS at the POTs Masterclass 2019
Dr Ravi Sargur presents 'Urinary Mast Cell Mediators in Mast Cell Disorders' as part of the BSACI webinar series 2021
Dr Arnold Deering talks about MCAS with Samia Qader
Diagnosis papers
Mast Cell Disorders Committee Work Group Report: Mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) diagnosis and management.
Weiler CR, Austen KF, Akin C, et al. AAAAI Mast Cell Disorders Committee Work Group Report: Mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) diagnosis and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144(4):883-896.
Recent advances in our understanding of mast cell activation–or should it be mast cell mediator disorders?. Expert review of clinical immunology.
Theoharides TC, Tsilioni I, Ren H. Recent advances in our understanding of mast cell activation–or should it be mast cell mediator disorders?. Expert review of clinical immunology. 2019 Jun 3;15(6):639-56.
Afrin LB, Ackerley MB, Bluestein LS, et al. Diagnosis of mast cell activation syndrome: a global 'consensus-2'
Afrin LB, Ackerley MB, Bluestein LS, et al. Diagnosis of mast cell activation syndrome: a global" consensus-2". Diagnosis (Berlin, Germany). 2020 Apr 22.
Weiler CR. Mast cell activation syndrome: tools for diagnosis and differential diagnosis.
Weiler CR. Mast cell activation syndrome: tools for diagnosis and differential diagnosis. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice. 2020 Feb 1;8(2):498-506.
Info on Recent International Disease Code (ICD10) codification of MCAS
The coding of MCAS into the ICD-10 (American version) is an important step in gaining better recognition of MCAS.
Diagnostic tests

MCAS Testing for Healthcare Professionals
This leaflet details some of the tests used to diagnose MCAS, how to order and handle a sample and how to read the results.
Diagnosing MCAS Leaflet
A leaflet discussing diagnostic criteria, biomarker tests and important information for diagnosis.
The utility of measuring urinary metabolites of mast cell mediators in systemic mastocytosis and mast cell activation syndrome.
Butterfield J, Weiler CR. The utility of measuring urinary metabolites of mast cell mediators in systemic mastocytosis and mast cell activation syndrome. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice. 2020 Sep 1;8(8):2533-41.
"New" tests for MCAS available in the UK
Sheffield Protein Reference Unit tests for mast cell activation markers
Important information for diagnosis
Mediator Tests for MCAS
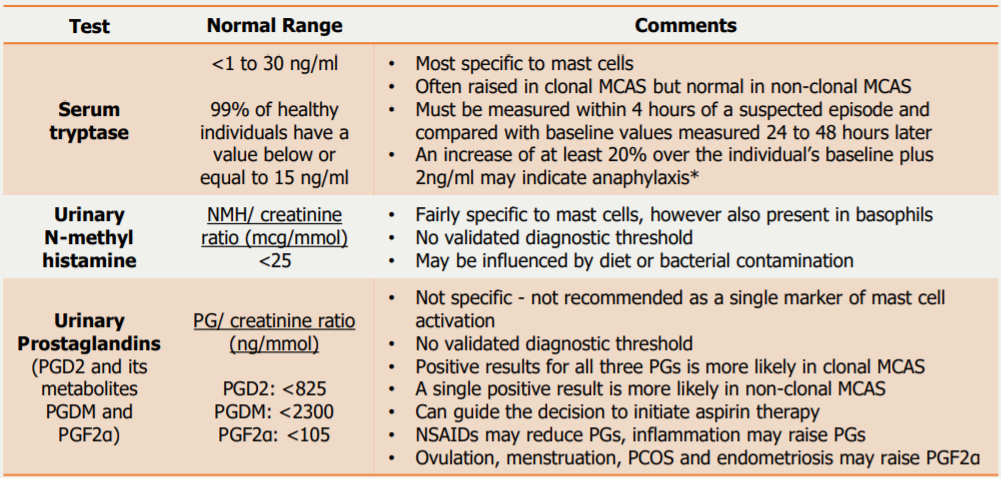
24-hour urine samples are recommended for assessing MCAS as mast cell mediators with short half lives may show normal results in spot urine samples.
Samples must be kept chilled throughout collection, storage and transport as many mast cell mediators are thermolabile.
Multiple tests are often conducted; ideally two abnormal biochemical values are required to diagnose MCAS.
MCAS patients may not have raised mast cell mediator levels unless they are symptomatic.
A positive result does not confirm MCAS, and a negative result is insufficient to rule out MCAS. Alongside test results, other diagnostic evidence should always be considered.
Treatment
Treatment Options
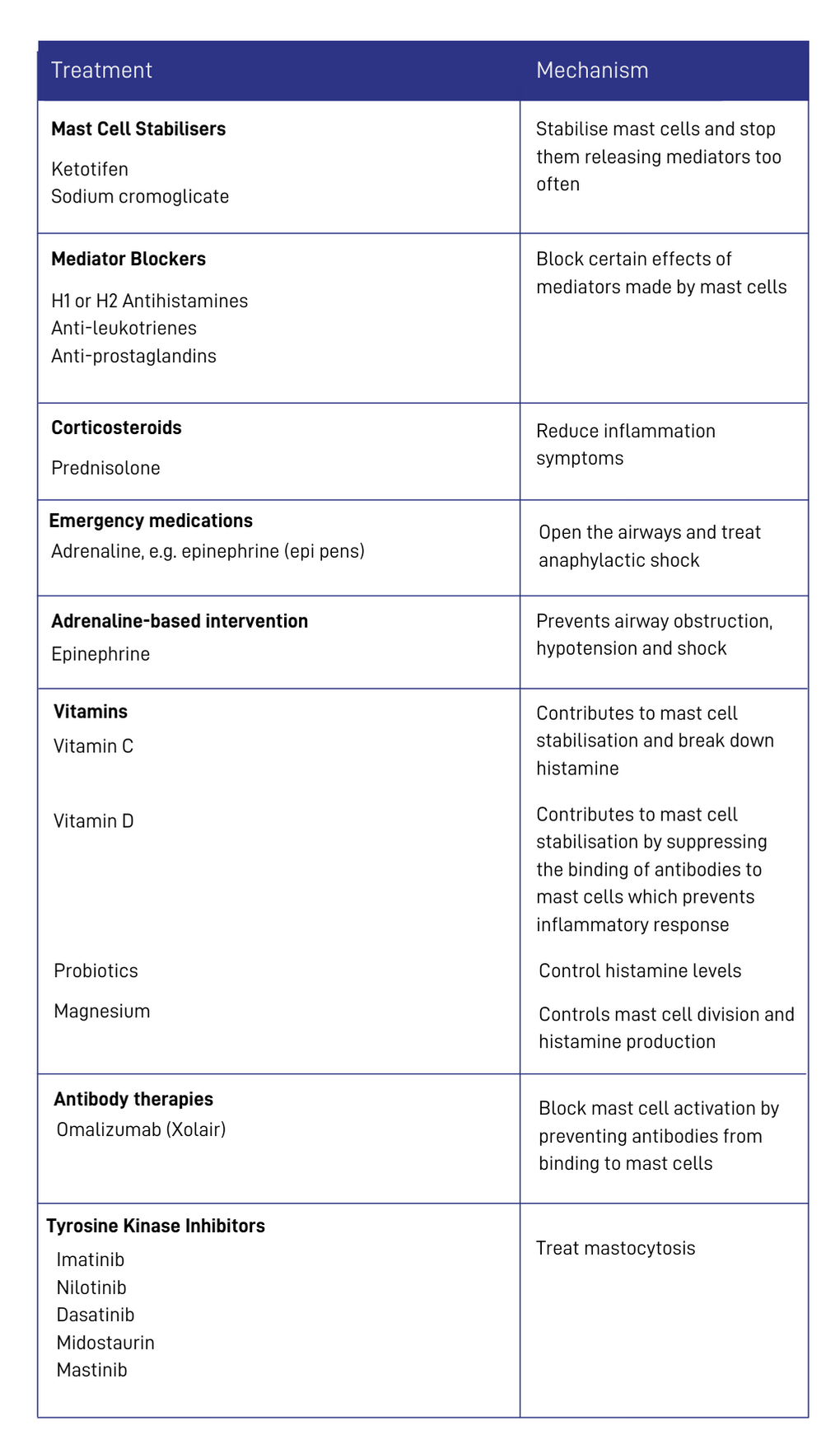
[A table showing the treatments used in mast cell activation diseases (including MCAS) and their mechanisms of action. Sources: Molderings GJ, Haenisch B, Brettner S, et al. Pharmacological treatment options for mast cell activation disease. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016;389(7):671-694. doi:10.1007/s00210-016-1247-1; Afrin LB, Butterfield JH, Raithel M, Molderings GJ. Often seen, rarely recognized: mast cell activation disease--a guide to diagnosis and therapeutic options. Ann Med. 2016;48(3):190-201. doi:10.3109/07853890.2016.1161231; Yip KH, Kolesnikoff N, Yu C, et al. Mechanisms of vitamin D₃ metabolite repression of IgE-dependent mast cell activation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133(5):1356-136514. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2013.11.030.]
Patient case examples
Where does MCAS fit in?
Mast Cell Related Disorders
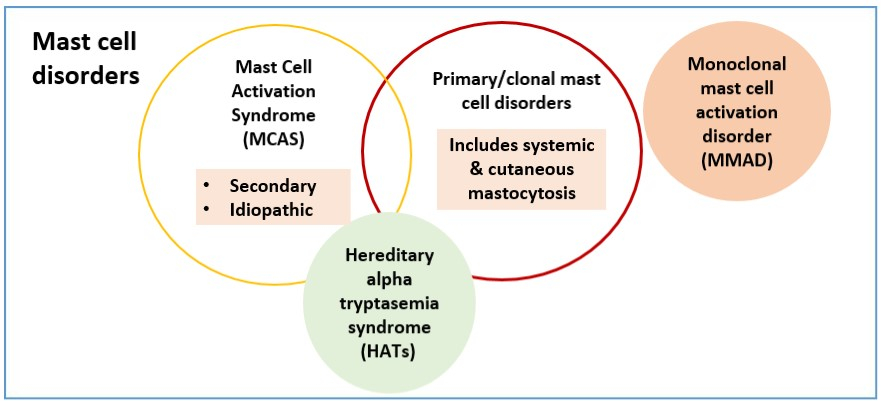
The three major forms of mast cell diseases are mastocytosis, mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), and hereditary alpha tryptasemia syndrome (HαTs).
MCAS can be categorised as primary, secondary or idiopathic. Primary MCAS (known as monoclonal mast cell activation disorder) falls under the primary mast cell disorders category alongside systemic and cutaneous mastocytosis. These disorders are characterised by hyperproliferative mast cells. On the other hand, secondary and idiopathic MCAS are non-clonal. Secondary MCAS occurs due to IgE-mediated or non-IgE mediated allergic reactions while idiopathic MCAS refers to MCAS in which no allergic or autoimmune cause can be found.
HαTs is a recently recognised condition. It commonly leads to elevated serum tryptase levels due to an increased copy number of the TPSAB1 gene.
Mast Cells and MCAS
Mediators
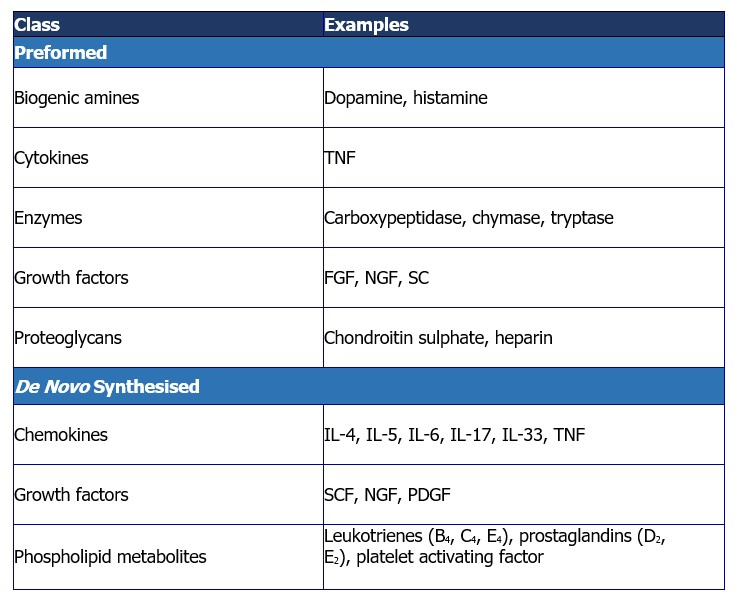
Mediators and Symptoms
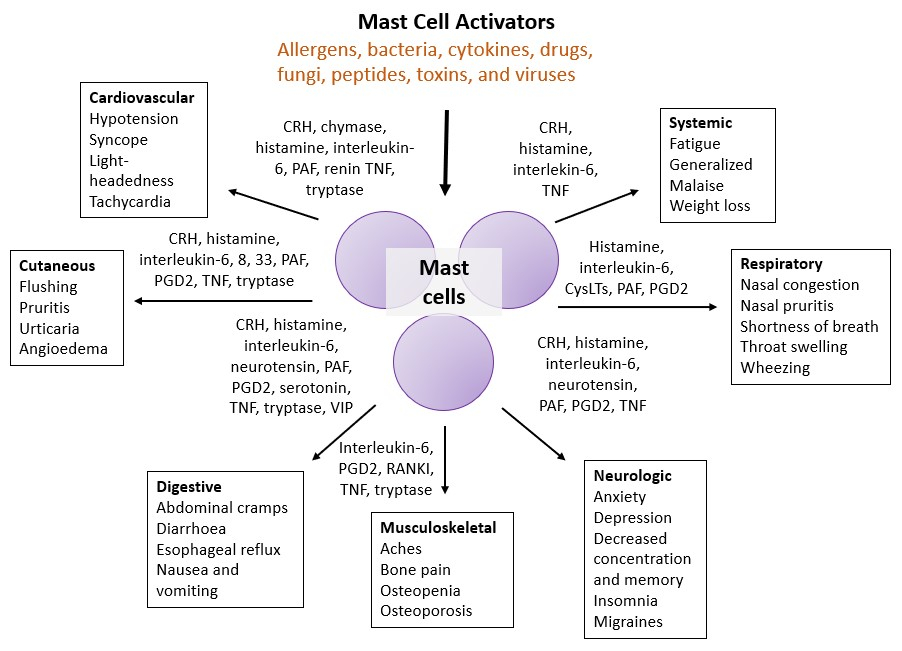
Pathways of mast cell mediator release
References
- Castells M. Mast cell mediators in allergic inflammation and mastocytosis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2006;26(3):465-485. doi:10.1016/j.iac.2006.05.005
- Dahlin, Joakim & Maurer, Marcus & Metcalfe, Dean & Pejler, Gunnar & Sagi-Eisenberg, Ronit & Nilsson, Gunnar. (2021). The Ingenious Mast Cell: Contemporary insights into mast cell behavior and function. Allergy. 10.1111/all.14881.
Theoharides TC, Valent P, Akin C. Mast Cells, Mastocytosis, and Related Disorders. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(2):163-72.
Theoharides TC, Tsilioni I, Ren H. Recent advances in our understanding of mast cell activation - or should it be mast cell mediator disorders?. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2019;15(6):639-656. doi:10.1080/1744666X.2019.1596800
[A table of mast cell-derived mediators. While some mediators are preformed and stored in granules, others are synthesised de novo. Source: Castells 2006, Theoharides et al. 2019.]
[A diagram showing the different symptoms associated with MCAS and the mast cell-derived mediators driving these symptoms. Figure adapted from Theoharides et al. 2015.]
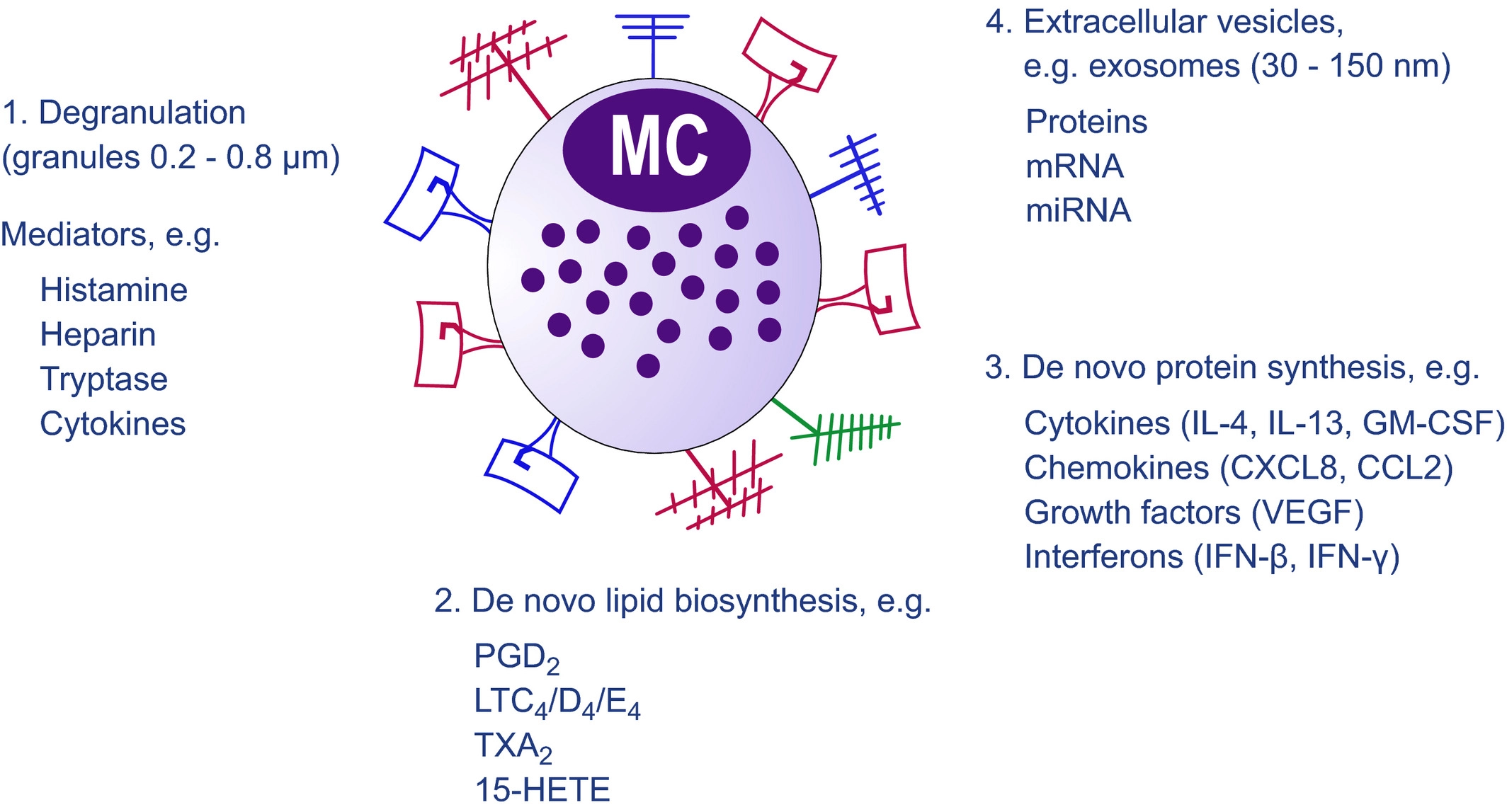
[A diagram showing the pathways by which mast cell-derived mediators are released. Upon recognition of endogenous and exogenous products by receptors, mast cells release mediators through one of several pathways: (1) degranulation and release of granules containing mediators such as histamine; (2) release of newly synthesized lipid mediators such as PGD2; (3) release of de novo-synthesized mediators such as cytokines; (4) release of extracellular vesicles, for example, exosomes. Figure taken from Dahlin et al. 2021.]
Become a friend
Sign up to become a Friend of Mast Cell Action so we can keep you up to date on our progress and on how to get involved in our latest campaigns and initiatives.
Donate
Mast Cell Action relies entirely on the generosity of people like you. Please make a donation now and together we can make a difference to those affected by MCAS.